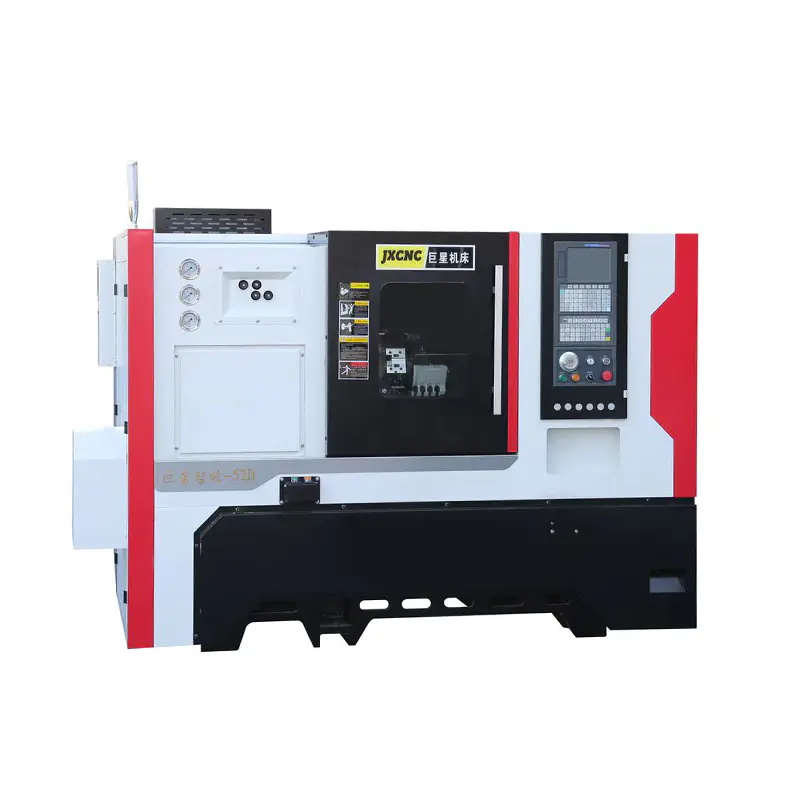
CNC polygon lathes are advanced machining tools used in the manufacturing of precision components with complex geometries. These machines are capable of turning non-circular shapes—such as hexagons, octagons, and other polygonal forms—on a workpiece. The effectiveness, precision, and longevity of a CNC polygon lathe largely depend on the materials used in its construction and the components involved in the machining process.

CNC polygon lathes, also known as CNC multi-edge lathes, are specialized machines designed to produce polygonal shapes with high precision. Unlike traditional lathes, which are typically used for turning circular shapes, CNC polygon lathes can create non-circular forms through a series of coordinated movements. The lathe's cutting tool moves in a precise, multi-faceted pattern, following the programmed instructions provided by the CNC system.
Polygon lathes are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and manufacturing, where components with non-circular cross-sections are required. These machines can produce parts such as shafts, bolts, and nuts, often with tight tolerances and complex geometries.
The materials used in CNC polygon lathes can be divided into two categories: the materials used for the machine's construction and the materials used for the cutting tools. Both of these categories are critical in determining the overall performance and longevity of the machine.
a) Materials for the Machine Structure
The frame and structural components of the CNC polygon lathe are designed to provide stability, strength, and rigidity. The materials used in the construction of the machine's frame, base, and support elements ensure that the machine can handle the stresses of operation without losing precision or accuracy.
Cast Iron: Cast iron is the commonly used material for the frame and base of CNC polygon lathes. Its high density provides vibration damping, which is important for maintaining accuracy during high-speed operations. Cast iron is also cost-effective and provides good stability under load, making it ideal for machines that require minimal deflection or movement during machining.
Steel: Steel is another commonly used material in the construction of CNC polygon lathes, particularly for parts that require additional strength and rigidity. Alloy steel is often used for components that experience high wear and tear, such as the bed and columns. Steel offers high tensile strength and ensures that the machine can withstand significant forces without compromising performance.
Welded Steel Plates: For larger CNC polygon lathes, welded steel plates are sometimes used to create the frame. This material is less heavy than cast iron but still provides the necessary rigidity. Welded steel frames also offer flexibility in terms of design, allowing manufacturers to create larger or more specialized machines as needed.
Aluminum Alloys: For smaller CNC polygon lathes or applications that require lighter machines, aluminum alloys are sometimes used. Aluminum is lightweight and has a good strength-to-weight ratio, but it is typically not as rigid or durable as steel or cast iron. However, for applications where precision is more important than handling heavy loads, aluminum alloys can provide an solution.
b) Materials for the Cutting Tools
The cutting tools in CNC polygon lathes are crucial for shaping the workpiece with high precision. These tools must be made from materials that can withstand the stresses of cutting and provide long-lasting performance. The materials chosen for the tools impact the machine's ability to achieve smooth, accurate cuts while maintaining sharpness over time.
High-Speed Steel (HSS): High-speed steel is one of the common materials used for cutting tools in CNC polygon lathes. It retains its hardness even at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for high-speed machining. HSS tools are durable, cost-effective, and suitable for machining a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, and brass.
Carbide: Carbide cutting tools are extremely hard and wear-resistant, making them ideal for high-performance CNC polygon lathes that need to machine tough materials or operate at high speeds. Tungsten carbide is often used for the tips of the cutting tools, as it provides durability and resistance to heat. Carbide tools are generally more expensive than HSS tools but offer performance and a longer lifespan, particularly for high-precision applications.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский